IOC-2: The use of computing innovations may involve risks to personal safety and identity.
Introduction
- Computing innovations have revolutionized how we communicate, work, and access information
- With this convenience comes significant risks to personal safety and identity
- Many digital services collect and store personal data, often without users being fully aware of the extent
- Hackers and malicious entities exploit vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information
- Understanding these risks and the methods used to protect computing resources is essential in the digital age
| Lesson Objective | Description |
|---|---|
| IOC-2.A | Describe the risks to privacy from collecting and storing personal data on a computer system. |
| IOC-2.B | Explain how computing resources can be protected and can be misused. |
| IOC-2.C | Explain how unauthorized access to computing resources is gained. |
IOC-2.A: Risks to Privacy from Collecting and Storing Personal Data
Personal Identifiable Information (PII)
«««< HEAD
- PII includes details relating to someone’s identity
- Includes (but is not limited to) full name, Social Security number, email address, and banking information
-
If exposed, it can lead to identity theft or fraud
3. Practice Safe Browsing (IOC Objective: Internet Safety)
The internet is a vast resource, but it also harbors risks. To browse safely:
- Avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading unknown files, as they may contain malware or lead to phishing sites.
- Verify website URLs before entering sensitive information. Look for typos or slight variations in domain names that could indicate a fake site.
- Use secure (HTTPS) websites for online transactions. The “S” in HTTPS stands for “secure,” indicating that the connection is encrypted.
- “Safe Computing Video”
545084c (FE)

How Data is Collected
- Search engines track queries and browsing habits.
- Social media platforms store interactions, personal details, and preferences
- Smart devices (phones, smart assistants, etc.) gather behavioral data for targeted advertising and service improvement
Google Lawsuit
“Alphabet’s Google has reportedly agreed to settle a class action lawsuit against it that claimed it secretly tracked the internet use of millions while on private browsing modes. The plaintiffs reportedly sought at least US$5 billion, alleging that the tech giant’s analytics, cookies, and apps enabled the Alphabet unit to track their activity even while on the Chrome browser’s “Incognito” mode and other browsers’ “private” modes.”
Aggregation of Disparate Data
Companies and organizations combine data from multiple sources to create detailed user profiles. For example, an advertising agency may collect location data from a phone app, social media interactions, and browsing history to target ads effectively.
- Google and Facebook ad targeting systems
- Google: collect data from watch history, searches, location
- Facebook: Collect info from user interactions, likes, third party apps

Misuse of Personal Data
- Stalking: Criminals can track individuals using public social media posts
- Identity Theft: Hackers use leaked credentials to commit fraud
- Criminal Activity: Malicious actors use online information to plan phishing scams or even physical crimes
HaveIBeenPwned
- Find out if your email was in a data breach
Popcorn Hack #1: Think about a website/company/app that has access to your PII. Describe the service and the kind of data they might store on you. Then, answer the question: How would it affect you if this information was stolen, and what might hackers be able to do with it? (Think about fraud, connections to other websites)
IOC-2.B: Protecting and Misusing Computing Resources
Authentication Measures
- Strong Passwords: Combining letters, numbers, and symbols increases security
- 123Qwerty! is an example of a strong password, containing numbers, capital and lowercase letters, and special characters
- Multifactor Authentication (MFA): Adds extra layers of security (more than 2)
- Examples: Biometric verification, secondary device verification, SMS code, email
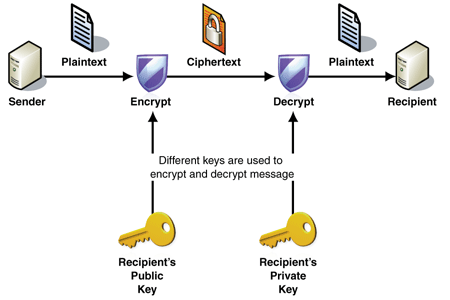
Encryption and Decryption
- Two main methods
- Symmetric Key Encryption: Uses the same key for encoding and decoding (e.g., AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) encryption in file security)
- Fast and efficient, but requires securely sharing the key between sender and recipient
- Public Key Encryption: Uses a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption (e.g., HTTPS securing website data exchanges)
- Public key can be shared openly but only recipient has access to the private key
Protection Against Malware
- Antivirus software detects and removes harmful programs
- Compares files and programs on a computer against a database of known malware signatures (characteristics)
- Looks for suspicious behaviors or code patterns, help detect new variants
- Monitors programs while they run, identifying actions typical of malware
- Sandboxing - Running program in controlled environment
- Regular software updates patch vulnerabilities that hackers may exploit
- Outdated software may be prone to newly discovered security flaws
Popcorn Hack #2: You receive an email warning that your bank account is locked and that you need to click a link to reset your password. What steps should you take before taking action?
IOC-2.C: Unauthorized Access to Computing Resources
Common Cyber Threats
- Phishing: Fraudulent emails or text messages that trick users into providing sensitive information

- Keylogging: Malicious software that records keystrokes to steal sensitive info
- usernames, passwords, credit card details
- can be installed through phishing attacks or malicious downloads
- Rogue Access Points: Hackers set up fake Wi-Fi networks to intercept data

- Malicious Links: Disguised as legitimate downloads, they install malware
Real-World Example
In 2021, a major pipeline company was targeted by a ransomware attack due to compromised credentials. The breach led to fuel shortages, demonstrating how unauthorized access can have widespread consequences.
- Colonial Pipeline
- Afflicted computerized equipment managing pipeline
- Overseen by FBI, company paid hackers 75 bitcoin ($4.4 million) for IT tool
- Likely started from breached employee personal password found on dark web
Popcorn Hack #3: How might public Wi-Fi networks be exploited by hackers, and what precautions should users take when connecting to them?
CollegeBoard Practice Exam Questions
2018 MCQs
- Q2 Bank Phishing Attempt: A bank customer receives an e-mail from a sender claiming to be a bank employee. The e-mail asks the customer to provide personal information and to call a phone number if he or she has any questions. The customer suspects the e-mail might be a phishing attempt. Which of the following responses is most likely to be a privacy risk for the bank customer?
- A) Calling the bank at its official phone number to ask whether the request for personal information is legitimate
- B) Calling the phone number given in the e-mail and providing the personal information over the phone
- C) Checking that the domain name of the sender’s e-mail address is associated with the bank
- D) Conducting a Web search to see if other people have received similar requests for personal information
Calling the phone number given in the e-mail and providing the personal information over the phone is the most significant privacy risk because phishing scams often use fake phone numbers to impersonate legitimate organizations. Attackers can then collect sensitive information, such as account numbers or passwords, and use it for fraudulent activities like identity theft or unauthorized transactions. Verifying the request by directly contacting the bank through its official phone number is a safer approach.
- Q47 Encrypting and decrypting using public key cryptography: In public key cryptography, the sender uses the recipient’s public key to encrypt a message. Which of the following is needed to decrypt the message?
- A) The sender’s public key
- B) The sender’s private key
- C) The recipient’s public key
- D) The recipient’s private key
The recipient’s private key is needed to decrypt the message because, in public key cryptography, encryption is performed using the recipient’s public key, which can be shared openly. However, only the corresponding private key—known only to the recipient—can decrypt the message. This ensures that even if someone intercepts the encrypted data, they cannot read it without access to the private key.
2020 MCQs
- Q9 Transmit private data securely: An Internet user has a need to send private data to another user. Which of the following provides the most security when transmitting private data?
- A) Certifying the data with a Creative Commons license before sending it
- B) Sending the data using a high-bandwidth connection
- C) Sending the data using public-key encryption
- D) Sending the data using redundant routing
Sending the data using public-key encryption is the correct answer because public-key encryption ensures that only the intended recipient, who possesses the corresponding private key, can decrypt and access the message. This method prevents unauthorized interception and protects data confidentiality, making it the most secure option for transmitting private information.
- Q48 Phishing scenario: Which of the following scenarios best exemplifies a phishing attack?
- A) A user connects to a public wireless network. An unauthorized individual intercepts data transmitted on the network, looking for private information that can be used to gain access to the user’s accounts.
- B) A user’s e-mail account is overwhelmed with messages containing large attachments, which causes the account to exceed the maximum amount of data allowed and temporarily prevents the user from sending and receiving new messages.
- C) A user receives an e-mail from a sender offering technical help with the user’s computer. The e-mail prompts the user to start a help session by clicking a provided link and entering the username and password associated with the user’s computer.
- D) A user chooses a weak password for an online account. An unauthorized individual successfully guesses the user’s password from a list of common passwords.
This exemplifies a phishing attack because the attacker is attempting to trick the user into providing sensitive credentials by pretending to offer legitimate technical assistance. Phishing attacks often use deceptive emails, fake websites, or urgent messages to manipulate users into revealing private information, such as login credentials, financial details, or personal data.
Homework MCQ
Which of the following is NOT considered PII?
- A) Social Security number
- B) Home address
- C) Favorite movie
- D) Email address
What is the purpose of multifactor authentication?
- A) Encrypting messages between two users
- B) Adding additional verification steps beyond a password
- C) Removing malware from an infected computer
- D) Allowing users to bypass login credentials
What is one way hackers can gain unauthorized access to personal information?
- A) Using keylogging software to record user keystrokes
- B) Encrypting user passwords for added security
- C) Using antivirus software to detect malware
- D) Sending software updates to fix vulnerabilities
How does public key encryption enhance security?
- A) By requiring multiple forms of identification
- B) By using the same key for both encryption and decryption
- C) By using separate keys for encryption and decryption
- D) By ensuring only one party can access encrypted data
Why should users be cautious when clicking links in emails?
- A) Links can lead to malware-infected websites or phishing scams
- B) Clicking links always results in identity theft
- C) Emails never contain safe links
- D) Links in emails slow down computers